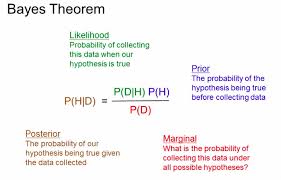
Bayes’ Theorem – Is the probability Event A will happen given (|) Event B happened.
P(A|B) = P(B|A) * P(A) / P(B)
For example (Assume we have 3 out of 4 probabilities):
Calculate a probability that an event A(Eating) will happen given (|) that an event B(Exercising) happened.
P(A|B) = P(B|A) * P(A) / P(B)
A = Eating
B = Exercising
P(A|B) = P(Eating given that Exercising happened) = (The Unknown)
P(B|A) =P(Exercising given that Eating happened) = 30%
P(A) = P(Eating) = 80%
P(B) = P(Exercising) = 50%
So, P(B|A) * P(A) / P(B) = 30%*80%/50% = 24%/50% = 48%
P(A|B) = 48%
Eating will happen 48% of the times given (|) that an event Exercising happened.